Hardness
Hardness is the measure of how resistant solid matter is to various kinds of permanent shape change when a force is applied. Macroscopic hardness is generally characterized by strong intermolecular bonds, however the behavior of solid materials under force is complex, therefore there are different measurements of hardness: scratch hardness, indentation hardness, and rebound hardness.
Hardness is dependent on ductility, elasticity, plasticity, strain, strength, toughness, viscoelasticity, and viscosity.
Common examples of hard matter are ceramics, concrete, metals, and superhard materials, which can be contrasted with soft matter.
Contents |
Measuring hardness

There are three main types of hardness measurements: scratch, indentation, and rebound. Within each of these classes of measurement there are individual measurement scales. For practical reasons conversion tables are used to convert between one scale and another.
Scratch hardness
Scratch hardness is the measure of how resistant a sample is to fracture or plastic (permanent) deformation due to friction from a sharp object. The principle is that an object made of a hard material will scratch an object made of a softer material. The most common test is Mohs scale, which is used in mineralogy. One tool to make this measurement is the sclerometer.
Indentation hardness
Indentation hardness measures the resistance of a sample to permanent plastic deformation due to a constant compression load from a sharp object; they are primarily used in engineering and metallurgy fields. The tests work on the basic premise of measuring the critical dimensions of an indentation left by a specifically dimensioned and loaded indenter.
Common indentation hardness scales are Rockwell, Vickers, and Brinell.
Rebound hardness
Rebound hardness, also known as dynamic hardness, measures the height of the "bounce" of a diamond-tipped hammer dropped from a fixed height onto a material. This type of hardness is related to elasticity. The device used to take this measurement is known as a scleroscope.[1]
Two scales that measures rebound hardness are the Leeb rebound hardness test and Bennett hardness scale.
Hardening
There are five hardening processes: Hall-Petch strengthening, work hardening, solid solution strengthening, precipitation hardening, martensitic transformation.
Physics

In solid mechanics, solids generally have three responses to force, depending on the amount of force and the type of material:
- They exhibit elasticity—the ability to temporarily change shape, but return to the original shape when the pressure is removed. "Hardness" in the elastic range—a small temporary change in shape for a given force—is known as stiffness in the case of a given object, or a high elastic modulus in the case of a material.
- They exhibit plasticity—the ability to permanently change shape in response to the force, but remain in one piece. The yield strength is the point at which elastic deformation gives way to plastic deformation. Deformation in the plastic range is non-linear, and is described by the stress-strain curve. This response produces the observed properties of scratch and indentation hardness, as described and measured in materials science. Some materials exhibit both elasticity and viscosity when undergoing plastic deformation; this is called viscoelasticity.
- They fracture—split into two or more pieces.
Strength is a measure of the extent of a material's elastic range, or elastic and plastic ranges together. This is quantified as compressive strength, shear strength, tensile strength depending on the direction of the forces involved. Ultimate strength is an engineering measure of the maximum load a part of a specific material and geometry can withstand.
Brittleness, in technical usage, is the tendency of a material to fracture with very little or no detectable deformation beforehand. Thus in technical terms, a material can be both brittle and strong. In everyday usage "brittleness" usually refers to the tendency to fracture under a small amount of force, which exhibits both brittleness and a lack of strength (in the technical sense). For perfectally brittle materials, yield strength and ultimate strength are the same, because they do not experience detectable plastic deformation. The opposite of brittleness is ductility.
The toughness of a material is the maximum amount of energy it can absorb before fracturing, which is different from the amount of force that can be applied. Toughness tends to be small for brittle materials, because it is elastic and plastic deformations that allow materials to absorb large amounts of energy.
Materials whose properties are different in different directions (because of an asymmetrical crystal structure) are referred to as anisotropic.
Hardness increases with decreasing particle size. This is known as the Hall-Petch relationship. However, below a critical grain-size, hardness decreases with decreasing grain size. This is known as the inverse Hall-Petch effect.
It is important to note that hardness of a material to deformation is dependent on its microdurability or small-scale shear modulus in any direction, not to any rigidity or stiffness properties such as its bulk modulus or Young's modulus. Scientists and journalists often confuse stiffness for hardness,[2][3] and spuriously report materials that are not actually harder than diamond because the anisotropy of their solid cells compromise hardness in other dimensions, resulting in a material prone to spalling and flaking in squamose or acicular habits in that dimension (e.g., osmium is stiffer than diamond but only as hard as quartz). In other words, a claimed hard material should have similar hardness characteristics at any location on its surface.
Mechanisms and theory

The key to understanding the mechanism behind hardness is understanding the metallic microstructure, or the structure and arrangement of the atoms at the atomic level. In fact, most important metallic properties critical to the manufacturing of today’s goods are determined by the microstructure of a material.[4] At the atomic level, the atoms in a metal are arranged in an orderly three-dimensional array called a crystal lattice. In reality, however, a given specimen of a metal likely never contains a consistent single crystal lattice. A given sample of metal will contain many grains, with each grain having a fairly consistent array pattern. At an even smaller scale, each grain contains irregularities.
There are two types of irregularities at the grain level of the microstructure that are responsible for the hardness of the material. These irregularities are point defects and line defects. A point defect is an irregularity located at a single lattice site inside of the overall three-dimensional lattice of the grain. There are three main point defects. If there is an atom missing from the array, a vacancy defect is formed. If there is a different type of atom at the lattice site that should normally be occupied by a metal atom, a substitutional defect is formed. If there exists an atom in a site where there should normally not be, an interstitial defect is formed. This is possible because space exists between atoms in a crystal lattice. While point defects are irregularities at a single site in the crystal lattice, line defects are irregularities on a plane of atoms. Dislocations are a type of line defect involving the misalignment of these planes. In the case of an edge dislocation, a half plane of atoms is wedged between two planes of atoms. In the case of a screw dislocation two planes of atoms are offset with a helical array running between them.[5]
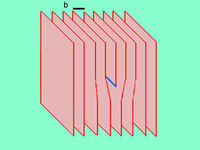
Dislocations provide a mechanism for planes of atoms to slip and thus a method for plastic or permanent deformation.[6] Planes of atoms can flip from one side of the dislocation to the other effectively allowing the dislocation to traverse through the material and the material to deform permanently. The movement allowed by these dislocations causes a decrease in the material's hardness.
The way to inhibit the movement of planes of atoms, and thus make them harder, involves the interaction of dislocations with each other and interstitial atoms. When a dislocation intersects with a second dislocation, it can no longer traverse through the crystal lattice. The intersection of dislocations creates an anchor point and does not allow the planes of atoms to continue to slip over one another[7] A dislocation can also be anchored by the interaction with interstitial atoms. If a dislocation comes in contact with two or more interstitial atoms, the slip of the planes will again be disrupted. The interstitial atoms create anchor points, or pinning points, in the same manner as intersecting dislocations.
By varying the presence of interstitial atoms and the density of dislocations, a particular metal's hardness can be controlled. Although seemingly counter-intuitive, as the density of dislocations increases, there are more intersections created and consequently more anchor points. Similarly, as more interstitial atoms are added, more pinning points that impede the movements of dislocations are formed. As a result, the more anchor points added, the harder the material will become.
See also
- Hardness of ceramics
- Toughness
- Schmidt hammer
Other strengthening mechanisms
- Grain boundary strengthening
- Precipitation hardening
- Solid solution strengthening
- Work hardening
References
- ↑ Allen, Robert (2006-12-10), A guide to rebound hardness and scleroscope test, http://www.articlestree.com/science/a-guide-to-rebound-hardness-and-scleroscope-test-tx301428.html, retrieved 2008-09-08
- ↑ Jeandron, Michelle (2005-08-25), "Diamonds are not forever", Physics World, http://physicsworld.com/cws/article/news/22997
- ↑ San-Miguel, A.; et al. (1999-05-19), "High Pressure Behavior of Silicon Clathrates: A New Class of Low Compressibility Materials", Physical Review 83 (25): 5290, doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.83.5290, http://link.aps.org/abstract/PRL/v83/p5290
- ↑ Haasen, P. (1978). Physical metallurgy. Cambridge [Eng.] ; New York: Cambridge University Press.
- ↑ Samuel, J. (2009). Introduction to materials science course manual. Madison, Wisconsin: University of Wisconsin-Madison.
- ↑ Haasen, P. (1978). Physical metallurgy. Cambridge [Eng.] ; New York: Cambridge University Press.
- ↑ Leslie, W. C. (1981). The physical metallurgy of steels. Washington: Hempisphere Pub. Corp ; New York: McGraw-Hill.
Further reading
- Dieter, George E. (1989). Mechanical Metallurgy (SI Metric Adaptation ed.). Maidenhead, UK: McGraw-Hill Education. ISBN ISBN 0-07-100406-8.
- Malzbender, J (2003). "Comment on hardness definitions". Journal of the European Ceramics Society 23: 1355. doi:10.1016/S0955-2219(02)00354-0.
- Chinn, R. L. (2009). Hardness, bearings, and the Rockwells. Advanced Materials & Processes, 167 (10), 29-31.
- Davis, J. R. (Ed.). (2002). Surface hardening of steels: Understanding the basics. Materials Park, OH: ASM International.
- Revankar, G. (2003). Introduction to hardness testing. Mechanical testing and evaluation, ASM Online Vol. 8.